Navigating China’s F&B Market: Key Growth Trends and Opportunities
China’s F&B market presents a dynamic landscape with substantial growth potential and evolving consumer preferences. Despite fierce competition, foreign companies are increasingly entering the Chinese market either through direct investment or partnerships with local firms. Adapting to the shifting market trends and fostering innovations are key to success in this dynamic market.
China’s food and beverage (F&B) market stands as one of the largest and fastest-growing sectors globally. This remarkable growth is fueled by increasing consumer spending, rapid urbanization, and the rise of a burgeoning middle class.
As consumers become more health-conscious and quality-driven, there is a notable shift towards healthier and premium products. Organic, low-sugar, and functional foods are gaining popularity, reflecting the evolving preferences of Chinese consumers.
Meanwhile, e-commerce is revolutionizing the F&B market, with online sales projected to account for 10 percent of total revenue by 2024. This digital transformation is providing consumers with greater convenience and access to a wider variety of products.
Despite facing challenges such as regulatory changes, food safety concerns, and intense competition, the market presents significant opportunities. Areas like plant-based foods, functional beverages, and innovative food technologies are ripe for growth. Additionally, China’s role as a major importer of food and beverage products highlights its growing interest in international cuisines and flavors.
Overview of China’s F&B market
Market size
China’s F&B market is vast and diverse, covering the entire supply chain from raw material supply, production, and processing to final consumption. In recent years, the market size of China’s F&B industry has continued to expand, demonstrating strong growth momentum. In 2023, the market size reached approximately RMB 11.71 trillion (US$1.67 trillion), representing a year-on-year growth of 3.75 percent. According to Statista, the F&B market in China is projected to grow annually by 7.38 percent from 2024 to 2029. Meanwhile, China’s food imports have been increasing steadily in recent years.
F&B imports
The country’s food imports grew from US$49 billion in 2013 to US$139.62 billion in 2022, registering an annual growth rate of 12.3 percent. The country has become the world’s largest food importer of food.
China’s top six imported food categories included meat and processed meat, grains and products made with processed grains, aquatic products, fruits and fruit products, dairy products, and vegetable oil, with the import value of each category exceeding US$10 billion, the report said. Imports of all these categories accounted for 79.1 percent of China’s total food imports.
Among the top sources of food imports, the leading countries were the United States, Brazil, and New Zealand. In 2022, the U.S. led with an import value of US$16.85 billion, accounting for 12.1 percent of China’s total food imports. Brazil followed with an import value of US$12.85 billion, reflecting a 23.1 percent increase and comprising 9.2 percent of the total. New Zealand ranked third with US$10.89 billion in imports, a 4.3 percent increase, representing 7.8 percent of China’s total food import value.
Industrial structure
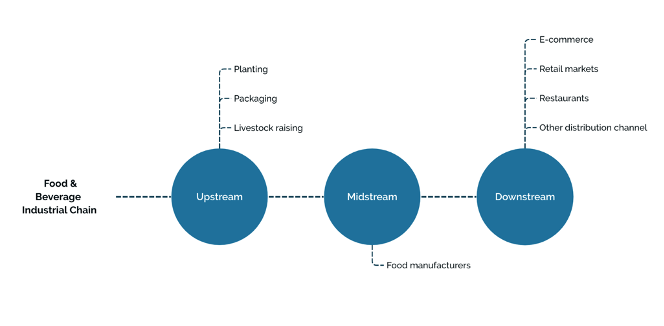
China’s F&B industry can be categorized into three segments: upstream, midstream, and downstream. The upstream segment includes planting, packaging, and livestock raising. The midstream encompasses F&B manufacturers. The downstream involves e-commerce platforms, retail markets, restaurants, and other distribution channels. Each stage of this industrial chain experiences different trends and unique opportunities for growth and innovation.
Upstream
Among the upstream F&B sectors, technological advancements have transformed food packaging from a simple protective measure during transportation to a significant marketing tool.
Packaging now plays a crucial role in influencing consumer behavior by serving as a direct channel for marketing content. This is especially relevant in the snack, instant food, and food delivery segments.
With the rise of younger consumers, the packaging industry is adapting to the “appearance economy” by incorporating eye-catching, customized, and co-branded designs. E-commerce platforms, which are increasingly popular, require higher packaging standards in terms of durability and consistency due to long-distance transportation and varying environmental conditions. Currently, approximately 51 percent of food packaging materials are plastic, 25 percent are paper, 20 percent are metal, and less than 10 percent are glass.
Meanwhile, sustainability is becoming a significant driver in the packaging industry. There is a growing emphasis on reducing environmental pollution by utilizing biodegradable and eco-friendly materials. Technological advancements, including the development of natural polymers, recyclable materials, and nanotechnology, are expected to shape the future of food packaging.
Recyclable and eco-friendly packaging materials are anticipated to become a major trend, with a strong focus on green packaging and advanced technologies.
Midstream
The midstream sector is dominated by food manufacturers, with significant representation from alcohol, dairy, and beverage segments. According to the Food & Beverage Innovation Forum 2023 (FBIF), 29 percent of China’s leading F&B companies are in the alcohol category, followed by 15 percent in dairy, 14 percent in beverages, 10 percent in seasoning, and 8 percent in snacks. The top 10 F&B manufacturers in this sector are as follows:
|
FDI in Canada by Ultimate Investor Country – China |
||||
| Rank in 2023 | Rank in 2022 | Company | Main category of the products | Scale of the value (100 million RMB) |
| 1 | 2 | Kweichow Moutai (贵州茅台) | Alcohol | 1238 |
| 2 | 1 | Yili Group (伊利集团) | Diary | 1211 |
| 3 | 4 | WH Group (万洲国际) | Meat | 1014 |
| 4 | 3 | Mengniu Dairy (蒙牛集团) | Diary | 926 |
| 5 | 5 | Master Kong (康师傅) | Multiple | 780 |
| 6 | 6 | Wuliangye (五粮液) | Alcohol | 675 |
| 7 | 7 | Hangzhou Wahaha Group (娃哈哈) | Beverage | 512 |
| 8 | 8 | ShanDong Luhua Group Co.,Ltd. (山东鲁花集团有限公司) | Vegetable oil | 468 |
| 9 | 9 | China Resources Breweries (华润啤酒) | Alcohol | 352 |
| 10 | 10 | Nongfu Spring (农夫山泉) | Beverage | 332 |
Within the alcohol category, Baijiu (Chinese liquor) is particularly dominant due to its cultural and social significance. Brands like Kweichow Moutai are expanding their reach to younger consumers with innovative products such as Maotai Ice Cream. In the first quarter of 2024, Maotai Ice Cream’s revenue increased by 239.62 percent year-over-year, and the company opened 35 flagship stores, marking a 48 percent year-over-year increase.
Dairy producers, too, are experiencing significant shifts as they innovate to meet market demands. Following challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic, the dairy industry has rebounded swiftly. In 2023, China’s total milk production reached 42.81 million tons, representing a 6.3 percent increase from the previous year. The demand for dairy products is expanding beyond liquid milk to include goat milk, dried milk powder, cheese, and butter, driven by increasing health-consciousness among Chinese consumers.
The beverage sector, particularly the refined tea, has seen dramatic growth. Flavors, functions, and nutritional benefits are key drivers of this segment. Established brands such as Wahaha and Nongfu Spring lead the market. These companies have diversified their product lines to include a variety of juices, ready-to-drink (RTD) teas, and energy drinks. Additionally, cultural identity is becoming an important factor, with RTD drinks incorporating traditional Chinese health concepts such as nourishing the stomach and clearing internal heat. In addition, as an increasing number of consumers pay attention to self-care, zero sugar drinks are the fastest expanding RTD in the demand market.
Downstream
In the downstream sector, e-commerce has become a major distribution channel. Online platforms now offer a wide range of products, from groceries to snacks and beverages, catering to diverse consumer preferences. As regional food products gain popularity, e-commerce platforms play a crucial role in their national distribution.
Key growth driver of China’s F&B market
The rapid development of the national economy, the promotion of consumption upgrade policies, and the continuous growth of consumer demand are driving the market. With the increase in per capita disposable income and changes in consumption concepts, consumers’ requirements for the quality, taste, and nutrition of food and beverages are rising, promoting industry innovation and upgrading. Additionally, the acceleration of urbanization and changes in population structure provide broader development space for the food and beverage market.
Urbanization
In examining the market growth drivers for China’s F&B industry, the role of consumer behavior stands out prominently. One critical demographic trend is the anticipated urbanization of China’s population, with projections indicating that 74 percent of the population will reside in urban areas by 2035. This shift is expected to significantly impact food consumption patterns, as urban residents typically demand more convenient and processed food options due to their fast-paced lifestyles. As a result, the industry is likely to see increased demand for products that align with the needs of an urbanized population seeking efficiency without compromising food quality.
Shifting consumption habits
Another influential factor in the market growth is the evolving eating habits of Chinese consumers. There is a notable shift towards healthier dietary preferences, with consumers increasingly prioritizing zero-sugar/low-fat, high-nutritious, non-GMO (genetically modified organism), and functional foods.
This growing inclination towards health-conscious eating presents substantial opportunities for foreign brands that emphasize high-quality, health-centric products can offer organic and functional foods to leverage this trend to cater to a market that is becoming more aware of and interested in the nutritional benefits of their food choices.
E-commerce and digitalization
The rise of e-commerce and digitalization is another significant driver shaping the F&B industry in China. Platforms such as Alibaba, Tmall, and JD.com have transformed the traditional retail landscape, offering a new way for F&B products to reach consumers. The rapid growth of these digital marketplaces has created an efficient and direct channel for foreign companies to enter the Chinese market.
By utilizing these platforms, international brands can overcome traditional distribution barriers and connect with a vast consumer base more effectively.
As Generation Z has entered the market and emerged as a key consumer demographic, their lifestyles, heavily influenced by social media, are becoming a focal point for midstream food manufacturers seeking innovation. This generation’s preferences and behaviors, shaped by rapid digital interactions and ever-changing trends, present new opportunities for product development. The pervasive presence of social media and the fast-paced evolution of fashion trends will continue to drive Chinese consumers toward more diverse and higher-quality products. Growth forecast
Trend in development
Shift toward premiumization
With rising disposable incomes, Chinese consumers are increasingly inclined to invest in high-quality, safe, and branded food products. This shift is particularly pronounced in the dairy, beverages, and snack segments, where high-quality and high-nutritious products are starting to gain an increasing market share. In urban areas where basic hunger needs have been largely met, social media trendy foods, low-calorie products, and premium snacks are increasingly occupying retail shelves and e-commerce platforms. In the future, health-oriented foods will become increasingly important to Chinese consumers. This trend is already evident in categories such as RTD tea, dairy products, and fruits.
Plant-based and alternative proteins
There is a growing demand for plant-based and alternative protein products, driven by health-conscious consumers and concerns about environmental sustainability. This trend mirrors global movements towards more sustainable and health-oriented diets. In China’s developed regions and first-tier cities, young professionals, influenced by a fast-paced lifestyle and the blending of global cultures, are increasingly focusing on food ingredients to meet their health and taste needs. In recent years, products such as soy-based items and plant-based milks have become increasingly popular, particularly in the beverage sector. China presents a promising market with expanding opportunities, as both consumers and regulatory frameworks increasingly support these innovative food options.
Tea, coffee, and alcoholic beverages
The market for tea, coffee, and alcoholic beverages is experiencing dynamic changes, marked by rapid innovation in flavors and product offerings. Leading brands are continuously introducing new flavors and engaging in co-branding initiatives with luxury and popular brands. This trend is fueled by a fast-paced work environment that demands convenient and stimulating beverage options. The sector’s evolution is characterized by an ongoing revolution in drink ingredients and preparation methods, driven by both consumer preferences and technological advancements.
Opportunities, challenges, and suggestions to foreign investors
China’s F&B market is characterized by its vast scale, rapid growth, and diverse consumer demands. That said, foreign investors entering this market may face multiple challenges, including competition from local enterprises, cultural adaptation, a complex regulatory environment, supply chain and logistics issues, and changing consumer preferences.
As the market continues to evolve, foreign businesses must adapt to changing trends and leverage innovation to succeed in this dynamic environment.
Adapting to local preferences
Foreign companies can achieve success in the Chinese market by tailoring their products to fit local tastes and dietary habits. For example, Starbucks has successfully adapted its offerings to local preferences by introducing the RTD “Pink Drink” series, a bottled version of its popular in-store beverage. This series, which includes flavors like Pink Drink, Mango Dragon Fruit Lemonade, and Strawberry Acai Lemonade, was initially a hit at Starbucks locations and has now been successfully introduced to the RTD market in China. By leveraging the popularity of these drinks and aligning them with local consumer tastes, Starbucks has expanded its market reach and established itself as a leader in the RTD coffee segment.
Focusing on healthy, high-quality products
Creating premium, high-quality products that meet the expectations of Chinese consumers can drive success. The pandemic has accelerated Chinese consumers’ awareness of health, leading to a surge in demand for high-quality, healthy imported foods. Taking fruits as an example, consumer preferences have shifted significantly in recent years. There has been a move from favoring ordinary domestic fruits, price sensitivity, and a preference for products with a long shelf life, towards a growing demand for imported fruits with shorter shelf lives but higher value. This trend is evident with seasonal fruits like cherries in winter and durians in summer. As the world’s largest consumer market for cherries, more than 80 percent of cherries consumed in China now come from Chile.
Leveraging e-commerce
The development of e-commerce has provided diversified sales channels for imported food, including traditional e-commerce platforms, cross-border e-commerce platforms, and new retail models. These platforms have significantly boosted the sales of imported food by optimizing user experience and improving logistics efficiency. For foreign investors, adapting to this trend is crucial for expanding into the Chinese market.
Investing in upstream manufacturing
Foreign investors can benefit from investing in China’s domestic upstream manufacturing sectors, such as planting and packaging. The upstream F&B industries in China’s food sector are experiencing active development and innovation, which means that equipment, technology, and high-end talent will become unavoidable elements of demand. Investing in these areas of technology is likely to yield higher returns through increased retail sales.
About Us
China Briefing is one of five regional Asia Briefing publications, supported by Dezan Shira & Associates. For a complimentary subscription to China Briefing’s content products, please click here.
Dezan Shira & Associates assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Haikou, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. We also have offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Dubai (UAE) and partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh, and Australia. For assistance in China, please contact the firm at china@dezshira.com or visit our website at www.dezshira.com.
- Previous Article China’s August 2024 Economy: Record Export Growth Amid Domestic Challenges
- Next Article